The use of the grounding system in Ex environments
It happened at least once to all to receive an electrostatic shock getting off the car and touching the door handle to close it. If we are...
It happened at least once to all to receive an electrostatic shock getting off the car and touching the door handle to close it. If we are not insulated from the ground (bringing rubber shoes), the static energy accumulated while standing on an insulated car discharges to earth through our body, coming into contact with the ground.
To prevent this phenomenon, it's possible to add to the car a conductive strip that, being always in contact with the ground, allows to instantly discharged the stored energy, thus avoiding the use of our body as the conduction element.
In potentially explosive atmospheres these phenomena occur during loading and/or unloading operations of vehicles that carry inflammable and explosives products, such as tank trucks for transport by road or LNG carriers for transport by sea.
However, it’s not enough to use a ground connection between the tanker and the ground network system, but it’s necessary to adopt security measures that connect the two systems safely, ensuring the safety of people and the protection of the property. Such systems are commonly referred as "grounding systems" and operate putting metallic conductors and semiconductors objects equipotential during the stages of loading or unloading of potentially explosive products.
For this reason, the grounding systems must be designed so as to ensure all the functionality of the system and, at the same time, guarantee the safety of operators in charge, in accordance with the compulsory regulations in that matter.
What can be the dangerous environments in which a grounding system is needed?
A. The loading/unloading bays tankers
B. The Jetty at sea, for the loading/unloading of oil tankers, gas tankers or gas carriers
C. Silos for liquid or solid products pouring

Cortem Group grounding device, GRD-4200 series, meets all the functionality and safety specifications required by the regulations for such operations and it is built to be installed in environments with danger of explosion due to gases and/or dusts.
As an indication only, we give below the description of a typical operating sequence for loading/unloading of a tanker in the loading/unloading bay. After positioning the tanker under the loading/unloading shelter, proceed with the operational sequence of our grounding system GRD-4200 series, such as described below:
- Activation of the "earthing system", with the verification of its functionality (red light on)
- Connect the device to the grounding system of the installation (if not already connected)
- Connect the grounding clamp of the device to the ground point of the tanker
- Turn the selector on the device in the "Start" position keeping it in position for not less than two seconds
- Verify that the green light has turned on and consequently the red light has turned off, and if the green light is on, release the selector referred to pos. 4
- The device is properly inserted and the tanker is equipotential with the main plant ground system
- The device, via a signaling contact of functional status, send to the control room or to the loading/unloading bay management system, the signal "Ready to dispense", in order to enable the loading system to operate with the opening of the inlet valve and activate the loading pump.
- During the entire loading/unloading phase, the device monitors the status of equipotentiality of the grounding system and, if the value, between 0 and 40 ohm, should be exceeded, provides to remove the consent of operation of the upload pump and close the inlet valve.
- In the latter case, the operator must verify that the ground connection has not been tampered and control the functionality of the system, with the restoration of the initial conditions.
- At the end of the loading/unloading operations, must be removed the connection hose to the tanker and unplug the grounding system between tanker and earthing system, by turning off the device and then disconnecting the ground wire from the tanker.
One of the peculiarities of our system is the special "clamp” that prevents the formation of sparkles in contaminated areas, thanks two "Ex d" micro chambers which avoids the spark propagation in the connection phase between the two systems.
This is obviously not enough to ensure a proper connection. For this reason, the electronics of our system is equipped with a protection and verify circuit that measures the resistance value and compares it with the parameter pre-set at the factory. If this value is within the range pre-set, it closes the electric circuit between the two equipotential systems.
For this approval, our test laboratory analysed the correct functionality, according to the HAZOP method (HAZard and OPerability Analysis), following a flowchart as reported below.
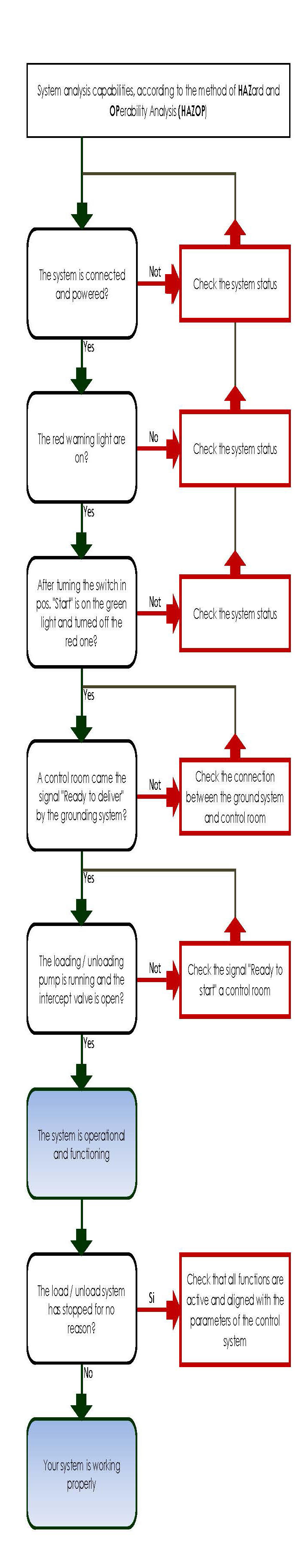
This analysis allowed us to test the device by a certifying body, in order to obtain a certification responsive to safety requirements (SIL), in accordance with the relevant EN 61508 and EN 50495 standards, mandatory for the compliance with the minimum safety and health requirements for industries, including thus all the chemical and petrochemical.
The certification has ratified that our "Grounding device" GRD-4200 series meets all the requirements for "SIL 2" Level (certification TUV No. C-IS-252099-01).
We conclude this short essay saying that our grounding device, GRD-4200 series meets all functional and safety specifications required by the regulations for such operations and it is built to be installed in environments at risk of explosion due to the presence of gases and/or dusts. We recommend to operators to comply with all rules laid down in our Use and Safety Instructions always attached to our product.